NEW DELHI — As India celebrates her 73rd year of independence from British rule, ragged children thread their way through traffic in Delhi, selling outsized national flags and souvenirs that say, “Mera Bharat Mahan.” My India is Great. Quite honestly, it’s hard to feel that way right now, because it looks very much as though our government has gone rogue.
Last week it unilaterally breached the fundamental conditions of the Instrument of Accession, by which the former Princely State of Jammu and Kashmir acceded to India in 1947. In preparation for this, at midnight on Aug. 4, it turned all of Kashmir into a giant prison camp. Seven million Kashmiris were barricaded in their homes, internet connections were cut and their phones went dead.
On Aug. 5, India’s home minister proposed in Parliament that Article 370 of the Indian Constitution (the article that outlines the legal obligations that arise from the Instrument of Accession) be overturned. The opposition parties rolled over. By the next evening the Jammu and Kashmir Reorganization Act, 2019 had been passed by the upper as well as the lower house.
The act strips the State of Jammu and Kashmir of its special status — which includes its right to have its own constitution and its own flag. It also strips it of statehood and partitions it into two Union territories. The first, Jammu and Kashmir, will be administered directly by the central government in New Delhi, although it will continue to have a locally elected legislative assembly but one with drastically reduced powers. The second, Ladakh, will be administered directly from New Delhi and will not have a legislative assembly.
 \
\
Blockades on the streets of Srinagar, the largest city in Jammu and Kashmir, on Aug. 11.CreditAtul Loke for The New York Times
The passing of the act was welcomed in Parliament by the very British tradition of desk-thumping. There was a distinct whiff of colonialism in the air. The masters were pleased that a recalcitrant colony had finally, formally, been brought under the crown. For its own good. Of course.
Indian citizens can now buy land and settle in their new domain. The new territories are open for business. Already India’s richest industrialist, Mukesh Ambani, of Reliance Industries, has promised several “announcements.” What this might mean to the fragile Himalayan ecology of Ladakh and Kashmir, the land of vast glaciers, high-altitude lakes and five major rivers, barely bears consideration.
The dissolution of the legal entity of the state also means the dissolution of Article 35A, which granted residents rights and privileges that made them stewards of their own territory. So, “being open for business,” it must be clarified, can also include Israeli-style settlements and Tibet-style population transfers.
For Kashmiris, in particular, this has been an old, primal fear. Their recurring nightmare (an inversion of the one being peddled by Donald Trump) of being swept away by a tidal wave of triumphant Indians wanting a little home in their sylvan valley could easily come true.
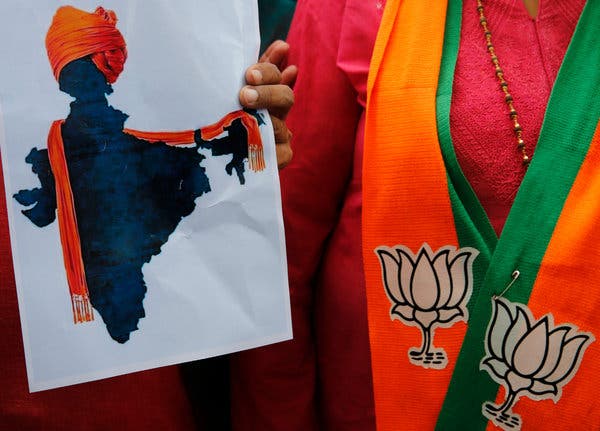

A supporter of India’s revocation of Kashmir’s special status displaying an artist's rendering of a map of India decorated with a shawl of saffron, the dominant color in the ruling Bharatiya Janata Party’s symbol.CreditRajesh Kumar Singh/Associated Press
As news of the new act spread, Indian nationalists of all stripes cheered. The mainstream media, for the most part, made a low, sweeping bow. There was dancing in the streets and horrifying misogyny on the internet. Manohar Lal Khattar, chief minister of the state of Haryana, bordering Delhi, while speaking about the improvement he had brought about in the skewed gender ratio in his state, joked: “Our Dhakarji used to say we will bring in girls from Bihar. Now they say Kashmir is open, we can bring girls from there.”
Amid these vulgar celebrations the loudest sound, however, is the deathly silence from Kashmir’s patrolled, barricaded streets and its approximately seven million caged, humiliated people, stitched down by razor wire, spied on by drones, living under a complete communications blackout. That in this age of information, a government can so easily cut off a whole population from the rest of the world for days at a time, says something serious about the times we are heading toward.
Kashmir, they often say, is the unfinished business of the “Partition.” That word suggests that in 1947, when the British drew their famously careless border through the subcontinent, there was a “whole” that was then partitioned. In truth, there was no “whole.” Apart from the territory of British India, there were hundreds of sovereign principalities, each of which individually negotiated the terms on which it would merge with either India or Pakistan. Many that did not wish to merge were forced to.
While Partition and the horrifying violence that it caused is a deep, unhealed wound in the memory of the subcontinent, the violence of those times, as well as in the years since, in India and Pakistan, has as much to do with assimilation as it does with partition. In India the project of assimilation, which goes under the banner of nation-building, has meant that there has not been a single year since 1947 when the Indian Army has not been deployed within India’s borders against its “own people.” The list is long — Kashmir, Mizoram, Nagaland, Manipur, Hyderabad, Assam.
The business of assimilation has been complicated and painful and has cost tens of thousands of lives. What is unfolding today on both sides of the border of the erstwhile state of Jammu and Kashmir is the unfinished business of assimilation.
What happened in the Indian Parliament last week was tantamount to cremating the Instrument of Accession. It was a document with a complicated provenance that had been signed by a discredited king, the Dogra Hindu King, Maharaja Hari Singh. His unstable, tattered kingdom of Jammu and Kashmir lay on the fault lines of the new border between India and Pakistan.
Advertisement
The rebellions that had broken out against him in 1945 had been aggravated and subsumed by the spreading bush fires of Partition. In the western mountain district of Poonch, Muslims, who were the majority, turned on the Maharaja’s forces and on Hindu civilians. In Jammu, to the south, the Maharaja’s forces assisted by troops borrowed from other princely states, massacred Muslims. Historians and news reports of the time estimated that somewhere between 70,000 and 200,000 were murdered in the streets of the city, and in its neighboring districts.
Inflamed by the news of the Jammu massacre, Pakistani “irregulars” swooped down from the mountains of the North Western Frontier Province, burning and pillaging their way across the Kashmir Valley. Hari Singh fled from Kashmir to Jammu from where he appealed to Jawaharlal Nehru, the Indian prime minister, for help. The document that provided legal cover for the Indian Army to enter Kashmir was the Instrument of Accession.
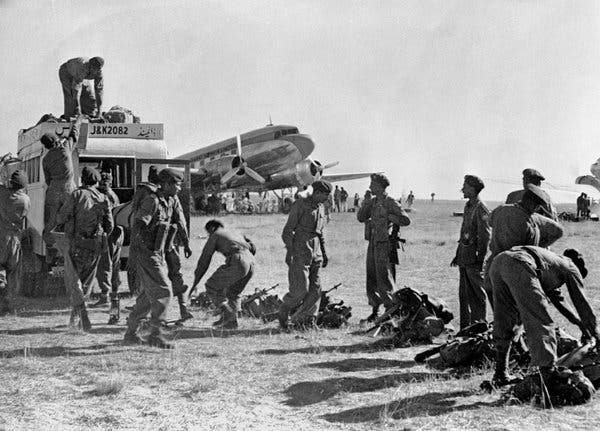

Indian soldiers, supplied by the British, arriving in Srinagar in 1947, to fight Pakistani troops for ownership of the Kashmir region.CreditBettmann Archive/Getty Images
The Indian Army, with some help from local people, pushed back the Pakistani “irregulars,” but only as far as the ring of mountains on the edge of the valley. The former Dogra kingdom now lay divided between India and Pakistan. The Instrument of Accession was meant to be ratified by a referendum to ascertain the will of the people of Jammu and Kashmir. That promised referendum never took place. So was born the subcontinent’s most intractable and dangerous political problem.
In the 72 years since then, successive Indian governments have undermined terms of the Instrument of Accession until all that was left of it was the skeletal structure. Now even that has been shot to hell.
It would be foolhardy to try to summarize the twists and turns of how things have come to this. Let’s just say that it’s as complicated and as dangerous as the games the United States played with its puppet regimes in South Vietnam all through the 50s and 60s.
After a long history of electoral manipulation, the watershed moment came in 1987 when New Delhi flagrantly rigged the state elections. By 1989, the thus far mostly nonviolent demand for self-determination grew into a full-throated freedom struggle. Hundreds of thousands of people poured onto the streets only to be cut down in massacre after massacre.
The Kashmir valley soon thronged with militants, Kashmiri men from both sides of the border, as well as foreign fighters, trained and armed by Pakistan and embraced, for the most part, by the Kashmiri people. Once again, Kashmir was caught up in the political winds that were blowing across the subcontinent — an increasingly radicalized Islam from Pakistan and Afghanistan, quite foreign to Kashmiri culture, and the fanatical Hindu nationalism that was on the rise in India.
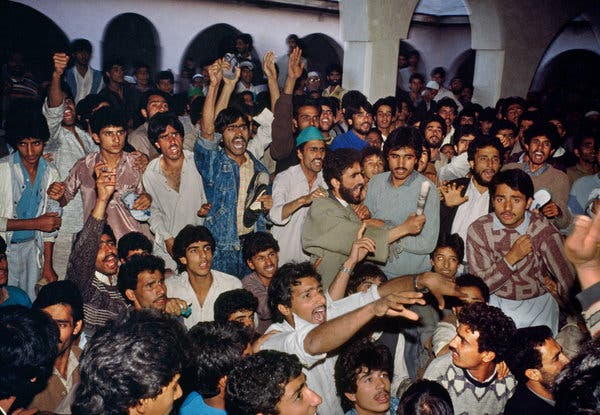
A heated debate among moderate and militant Kashmiri separatists at a mosque in Anantnag, Jammu and Kashmir, on Oct. 8, 1989, two years after the Jammu and Kashmir state legislative elections, which were said to have been rigged. CreditRobert Nickelsberg/Getty Images
The first casualty of the uprising was the age-old bond between Kashmir’s Muslims and its tiny minority of Hindus, known locally as Pandits. When the violence began, according to the Kashmiri Pandit Sangharsh Samiti, or the K.P.S.S., an organization run by Kashmiri Pandits, about 400 Pandits were targeted and murdered by militants. By the end of 1990, according to a government estimate, 25,000 Pandit families had left the valley.
They lost their homes, their homeland and everything they had. Over the years thousands more left — almost the entire population. As the conflict continued, in addition to tens of thousands of Muslims, the K.P.S.S. says 650 Pandits have been killed in the conflict.
Since then, great numbers of Pandits have lived in miserable refugee camps in Jammu city. Thirty years have gone by, yet successive governments in New Delhi have not tried to help them return home. They have preferred instead to keep them in limbo, and stir their anger and understandable bitterness into a mephitic brew with which to fuel India’s dangerous and extremely effective nationalistic narrative about Kashmir. In this version, a single aspect of an epic tragedy is cannily and noisily used to draw a curtain across the rest of the horror.

Security personnel on the streets of Srinagar last week.CreditAtul Loke for The New York Times
Today Kashmir is one of the most or perhaps the most densely militarized zone in the world. More than a half-million soldiers have been deployed to counter what the army itself admits is now just a handful of “terrorists.” If there were any doubt earlier it should be abundantly clear by now that their real enemy is the Kashmiri people. What India has done in Kashmir over the last 30 years is unforgivable. An estimated 70,000 people, civilians, militants and security forces have been killed in the conflict. Thousands have been “disappeared,” and tens of thousands have passed through torture chambers that dot the valley like a network of small-scale Abu Ghraibs.
Advertisement
Over the last few years, hundreds of teenagers have been blinded by the use of pellet-firing shotguns, the security establishment’s new weapon of choice for crowd control. Most militants operating in the valley today are young Kashmiris, armed and trained locally. They do what they do knowing full well that the minute they pick up a gun, their “shelf life” is unlikely to be more than six months. Each time a “terrorist” is killed, Kashmiris turn up in their tens of thousands to bury a young man whom they revere as a shaheed, a martyr.

Sameer Ahamed, a page designer for local newspapers, whose eyes and arms were injured from pellets, in Srinagar on Aug. 10. CreditAtul Loke for The New York Times
These are only the rough coordinates of a 30-year-old military occupation. The most cruel effects of an occupation that has lasted decades are impossible to describe in an account as short as this.
In Narendra Modi’s first term as India’s prime minister, his hard-line approach exacerbated the violence in Kashmir. In February, after a Kashmiri suicide bomber killed 40 Indian security personnel, India launched an airstrike against Pakistan. Pakistan retaliated. They became the first two nuclear powers in history to actually launch airstrikes against each other. Now two months into Narendra Modi’s second term, his government has played its most dangerous card of all. It has tossed a lit match into a powder keg.
If that were not bad enough, the cheap, deceitful way in which it did it is disgraceful. In the last week of July, 45,000 extra troops were rushed into Kashmir on various pretexts. The one that got the most traction was that there was a Pakistani “terror” threat to the Amarnath Yatra — the annual pilgrimage in which hundreds of thousands of Hindu devotees trek (or are carried by Kashmiri porters) through high mountains to visit the Amarnath cave and pay their respects to a natural ice formation that they believe is an avatar of Shiva.
On Aug. 1, some Indian television networks announced that a land mine with Pakistani Army markings on it had been found on the pilgrimage route. On Aug. 2, the government published a notice asking all pilgrims (and even tourists who were miles from the pilgrimage route) to leave the valley immediately. That set off a panicky exodus. The approximately 200,000 Indian migrant day laborers in Kashmir were clearly not a concern to those supervising the evacuation. Too poor to matter, I’m guessing. By Saturday, Aug. 3, tourists and pilgrims had left and the security forces had taken up position across the valley.

 www.nytimes.com
www.nytimes.com
Last week it unilaterally breached the fundamental conditions of the Instrument of Accession, by which the former Princely State of Jammu and Kashmir acceded to India in 1947. In preparation for this, at midnight on Aug. 4, it turned all of Kashmir into a giant prison camp. Seven million Kashmiris were barricaded in their homes, internet connections were cut and their phones went dead.
On Aug. 5, India’s home minister proposed in Parliament that Article 370 of the Indian Constitution (the article that outlines the legal obligations that arise from the Instrument of Accession) be overturned. The opposition parties rolled over. By the next evening the Jammu and Kashmir Reorganization Act, 2019 had been passed by the upper as well as the lower house.
The act strips the State of Jammu and Kashmir of its special status — which includes its right to have its own constitution and its own flag. It also strips it of statehood and partitions it into two Union territories. The first, Jammu and Kashmir, will be administered directly by the central government in New Delhi, although it will continue to have a locally elected legislative assembly but one with drastically reduced powers. The second, Ladakh, will be administered directly from New Delhi and will not have a legislative assembly.

Blockades on the streets of Srinagar, the largest city in Jammu and Kashmir, on Aug. 11.CreditAtul Loke for The New York Times
The passing of the act was welcomed in Parliament by the very British tradition of desk-thumping. There was a distinct whiff of colonialism in the air. The masters were pleased that a recalcitrant colony had finally, formally, been brought under the crown. For its own good. Of course.
Indian citizens can now buy land and settle in their new domain. The new territories are open for business. Already India’s richest industrialist, Mukesh Ambani, of Reliance Industries, has promised several “announcements.” What this might mean to the fragile Himalayan ecology of Ladakh and Kashmir, the land of vast glaciers, high-altitude lakes and five major rivers, barely bears consideration.
The dissolution of the legal entity of the state also means the dissolution of Article 35A, which granted residents rights and privileges that made them stewards of their own territory. So, “being open for business,” it must be clarified, can also include Israeli-style settlements and Tibet-style population transfers.
For Kashmiris, in particular, this has been an old, primal fear. Their recurring nightmare (an inversion of the one being peddled by Donald Trump) of being swept away by a tidal wave of triumphant Indians wanting a little home in their sylvan valley could easily come true.

A supporter of India’s revocation of Kashmir’s special status displaying an artist's rendering of a map of India decorated with a shawl of saffron, the dominant color in the ruling Bharatiya Janata Party’s symbol.CreditRajesh Kumar Singh/Associated Press
As news of the new act spread, Indian nationalists of all stripes cheered. The mainstream media, for the most part, made a low, sweeping bow. There was dancing in the streets and horrifying misogyny on the internet. Manohar Lal Khattar, chief minister of the state of Haryana, bordering Delhi, while speaking about the improvement he had brought about in the skewed gender ratio in his state, joked: “Our Dhakarji used to say we will bring in girls from Bihar. Now they say Kashmir is open, we can bring girls from there.”
Amid these vulgar celebrations the loudest sound, however, is the deathly silence from Kashmir’s patrolled, barricaded streets and its approximately seven million caged, humiliated people, stitched down by razor wire, spied on by drones, living under a complete communications blackout. That in this age of information, a government can so easily cut off a whole population from the rest of the world for days at a time, says something serious about the times we are heading toward.
Kashmir, they often say, is the unfinished business of the “Partition.” That word suggests that in 1947, when the British drew their famously careless border through the subcontinent, there was a “whole” that was then partitioned. In truth, there was no “whole.” Apart from the territory of British India, there were hundreds of sovereign principalities, each of which individually negotiated the terms on which it would merge with either India or Pakistan. Many that did not wish to merge were forced to.
While Partition and the horrifying violence that it caused is a deep, unhealed wound in the memory of the subcontinent, the violence of those times, as well as in the years since, in India and Pakistan, has as much to do with assimilation as it does with partition. In India the project of assimilation, which goes under the banner of nation-building, has meant that there has not been a single year since 1947 when the Indian Army has not been deployed within India’s borders against its “own people.” The list is long — Kashmir, Mizoram, Nagaland, Manipur, Hyderabad, Assam.
The business of assimilation has been complicated and painful and has cost tens of thousands of lives. What is unfolding today on both sides of the border of the erstwhile state of Jammu and Kashmir is the unfinished business of assimilation.
What happened in the Indian Parliament last week was tantamount to cremating the Instrument of Accession. It was a document with a complicated provenance that had been signed by a discredited king, the Dogra Hindu King, Maharaja Hari Singh. His unstable, tattered kingdom of Jammu and Kashmir lay on the fault lines of the new border between India and Pakistan.
Advertisement
The rebellions that had broken out against him in 1945 had been aggravated and subsumed by the spreading bush fires of Partition. In the western mountain district of Poonch, Muslims, who were the majority, turned on the Maharaja’s forces and on Hindu civilians. In Jammu, to the south, the Maharaja’s forces assisted by troops borrowed from other princely states, massacred Muslims. Historians and news reports of the time estimated that somewhere between 70,000 and 200,000 were murdered in the streets of the city, and in its neighboring districts.
Inflamed by the news of the Jammu massacre, Pakistani “irregulars” swooped down from the mountains of the North Western Frontier Province, burning and pillaging their way across the Kashmir Valley. Hari Singh fled from Kashmir to Jammu from where he appealed to Jawaharlal Nehru, the Indian prime minister, for help. The document that provided legal cover for the Indian Army to enter Kashmir was the Instrument of Accession.

Indian soldiers, supplied by the British, arriving in Srinagar in 1947, to fight Pakistani troops for ownership of the Kashmir region.CreditBettmann Archive/Getty Images
The Indian Army, with some help from local people, pushed back the Pakistani “irregulars,” but only as far as the ring of mountains on the edge of the valley. The former Dogra kingdom now lay divided between India and Pakistan. The Instrument of Accession was meant to be ratified by a referendum to ascertain the will of the people of Jammu and Kashmir. That promised referendum never took place. So was born the subcontinent’s most intractable and dangerous political problem.
In the 72 years since then, successive Indian governments have undermined terms of the Instrument of Accession until all that was left of it was the skeletal structure. Now even that has been shot to hell.
It would be foolhardy to try to summarize the twists and turns of how things have come to this. Let’s just say that it’s as complicated and as dangerous as the games the United States played with its puppet regimes in South Vietnam all through the 50s and 60s.
After a long history of electoral manipulation, the watershed moment came in 1987 when New Delhi flagrantly rigged the state elections. By 1989, the thus far mostly nonviolent demand for self-determination grew into a full-throated freedom struggle. Hundreds of thousands of people poured onto the streets only to be cut down in massacre after massacre.
The Kashmir valley soon thronged with militants, Kashmiri men from both sides of the border, as well as foreign fighters, trained and armed by Pakistan and embraced, for the most part, by the Kashmiri people. Once again, Kashmir was caught up in the political winds that were blowing across the subcontinent — an increasingly radicalized Islam from Pakistan and Afghanistan, quite foreign to Kashmiri culture, and the fanatical Hindu nationalism that was on the rise in India.
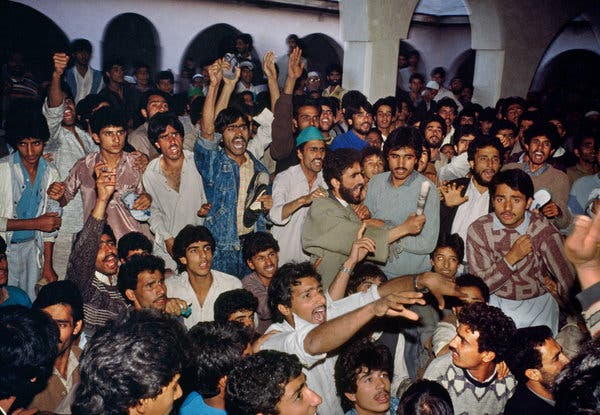
A heated debate among moderate and militant Kashmiri separatists at a mosque in Anantnag, Jammu and Kashmir, on Oct. 8, 1989, two years after the Jammu and Kashmir state legislative elections, which were said to have been rigged. CreditRobert Nickelsberg/Getty Images
The first casualty of the uprising was the age-old bond between Kashmir’s Muslims and its tiny minority of Hindus, known locally as Pandits. When the violence began, according to the Kashmiri Pandit Sangharsh Samiti, or the K.P.S.S., an organization run by Kashmiri Pandits, about 400 Pandits were targeted and murdered by militants. By the end of 1990, according to a government estimate, 25,000 Pandit families had left the valley.
They lost their homes, their homeland and everything they had. Over the years thousands more left — almost the entire population. As the conflict continued, in addition to tens of thousands of Muslims, the K.P.S.S. says 650 Pandits have been killed in the conflict.
Since then, great numbers of Pandits have lived in miserable refugee camps in Jammu city. Thirty years have gone by, yet successive governments in New Delhi have not tried to help them return home. They have preferred instead to keep them in limbo, and stir their anger and understandable bitterness into a mephitic brew with which to fuel India’s dangerous and extremely effective nationalistic narrative about Kashmir. In this version, a single aspect of an epic tragedy is cannily and noisily used to draw a curtain across the rest of the horror.

Security personnel on the streets of Srinagar last week.CreditAtul Loke for The New York Times
Today Kashmir is one of the most or perhaps the most densely militarized zone in the world. More than a half-million soldiers have been deployed to counter what the army itself admits is now just a handful of “terrorists.” If there were any doubt earlier it should be abundantly clear by now that their real enemy is the Kashmiri people. What India has done in Kashmir over the last 30 years is unforgivable. An estimated 70,000 people, civilians, militants and security forces have been killed in the conflict. Thousands have been “disappeared,” and tens of thousands have passed through torture chambers that dot the valley like a network of small-scale Abu Ghraibs.
Advertisement
Over the last few years, hundreds of teenagers have been blinded by the use of pellet-firing shotguns, the security establishment’s new weapon of choice for crowd control. Most militants operating in the valley today are young Kashmiris, armed and trained locally. They do what they do knowing full well that the minute they pick up a gun, their “shelf life” is unlikely to be more than six months. Each time a “terrorist” is killed, Kashmiris turn up in their tens of thousands to bury a young man whom they revere as a shaheed, a martyr.

Sameer Ahamed, a page designer for local newspapers, whose eyes and arms were injured from pellets, in Srinagar on Aug. 10. CreditAtul Loke for The New York Times
These are only the rough coordinates of a 30-year-old military occupation. The most cruel effects of an occupation that has lasted decades are impossible to describe in an account as short as this.
In Narendra Modi’s first term as India’s prime minister, his hard-line approach exacerbated the violence in Kashmir. In February, after a Kashmiri suicide bomber killed 40 Indian security personnel, India launched an airstrike against Pakistan. Pakistan retaliated. They became the first two nuclear powers in history to actually launch airstrikes against each other. Now two months into Narendra Modi’s second term, his government has played its most dangerous card of all. It has tossed a lit match into a powder keg.
If that were not bad enough, the cheap, deceitful way in which it did it is disgraceful. In the last week of July, 45,000 extra troops were rushed into Kashmir on various pretexts. The one that got the most traction was that there was a Pakistani “terror” threat to the Amarnath Yatra — the annual pilgrimage in which hundreds of thousands of Hindu devotees trek (or are carried by Kashmiri porters) through high mountains to visit the Amarnath cave and pay their respects to a natural ice formation that they believe is an avatar of Shiva.
On Aug. 1, some Indian television networks announced that a land mine with Pakistani Army markings on it had been found on the pilgrimage route. On Aug. 2, the government published a notice asking all pilgrims (and even tourists who were miles from the pilgrimage route) to leave the valley immediately. That set off a panicky exodus. The approximately 200,000 Indian migrant day laborers in Kashmir were clearly not a concern to those supervising the evacuation. Too poor to matter, I’m guessing. By Saturday, Aug. 3, tourists and pilgrims had left and the security forces had taken up position across the valley.

Opinion | The Silence Is the Loudest Sound (Published 2019)
The Indian government has confined about seven million Kashmiris to their homes and imposed a complete communications blackout.
Last edited by a moderator:


































