RiazHaq
Senator (1k+ posts)
https://www.riazhaq.com/2019/01/pakistan-garment-industry-becoming-more.html
Low wages and trade deals with Western nations have helped Bangladesh build a $30 billion ready-made garments (RMG) industry that accounts for 80% of country's exports. Bangladesh is the world's second largest RMG exporter after China. Rising monthly wages of Bangladesh garment worker in terms of US dollars are now catching up with the minimum wage in Pakistan, especially after recent Pakistani rupee devaluation. Minimum monthly wage in Pakistan has declined from $136 last year to $107 now while Bangladesh has seen it increase from $64 last year to $95 today. Western garment buyers, known for their relentless pursuit of the lowest labor costs, will likely diversify their sources by directing new investments to Pakistan and other nations. Competing on low cost alone may prove to be a poor long term exports strategy for both countries. Greater value addition with diverse products and services will be necessary to remain competitive as wages rise in both countries.
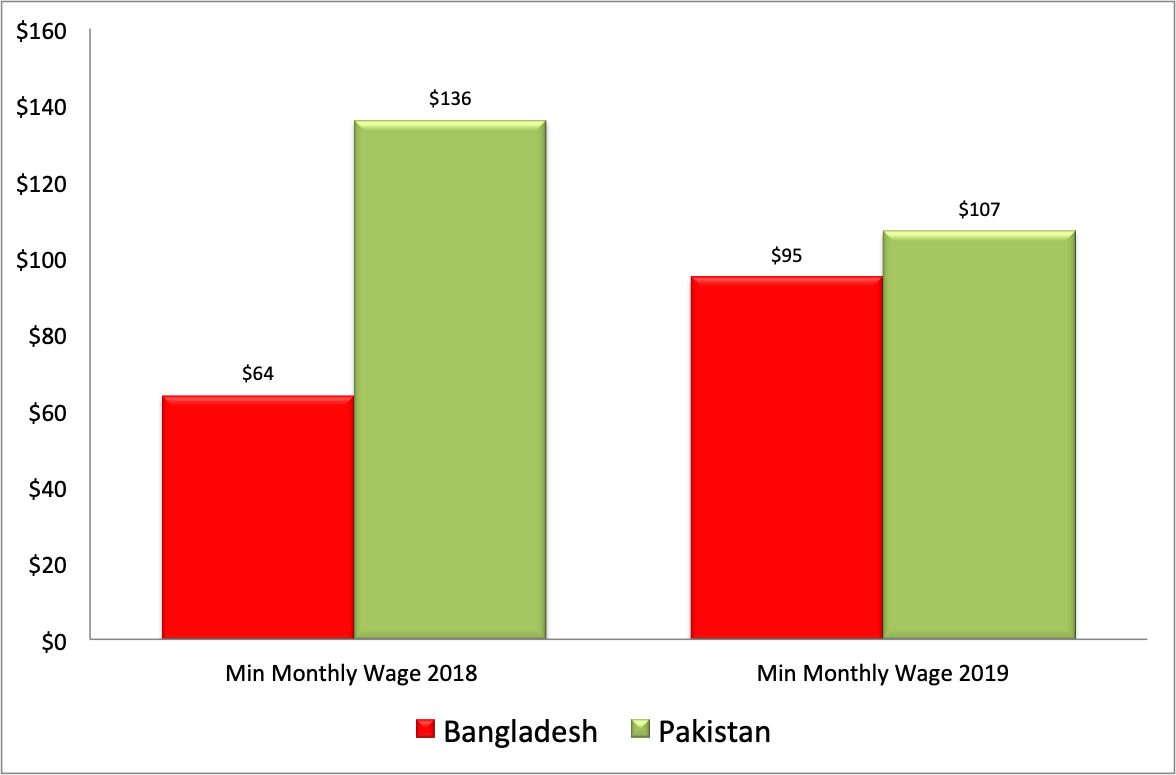
Minimum Monthly Wages in US$ Market Exchange Rate
Wage Hike in Bangladesh:
The government in Dhaka announced in September that the minimum wage for garment workers would increase by up to 51% this year to 8,000 taka ($95) a month, up from $64 a year ago, according to Renaissance Capital. But garment workers union leaders say that increase will benefit only a small percentage of workers in the sector, which employs 4 million in the country of 165 million people, according to Reuters. Bangladesh government promised this week it would consider demands for an increase in the minimum wage, after clashes between police and protesters killed one worker and wounded dozens.
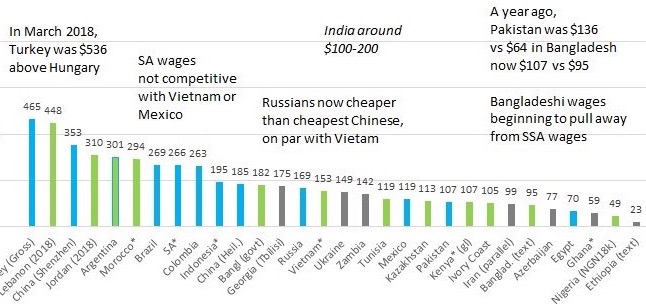
Monthly Minimum Wages in US$. Source: Renaissance Capital
Pakistan Wage Decline:
Pakistani currency has seen about 25% decline in value against the US dollar since January 2018. As a result of this devaluation, the minimum monthly wage in Pakistan has dropped from $136 last year to $107 now while Bangladesh has seen it increase from $64 last year to $95 today. Renaissance Capital projects a further 10% depreciation in Pakistani rupee this year.
Race to the Bottom?
Competing on cost alone is like engaging in the race to the bottom. Neither Pakistan nor Bangladesh can count on being lowest cost producers in the long run. What must they do to grow their exports in the future? The only viable option for both is to diversify their products and services and add greater value to justify higher prices.
Pakistan's Export Performance:
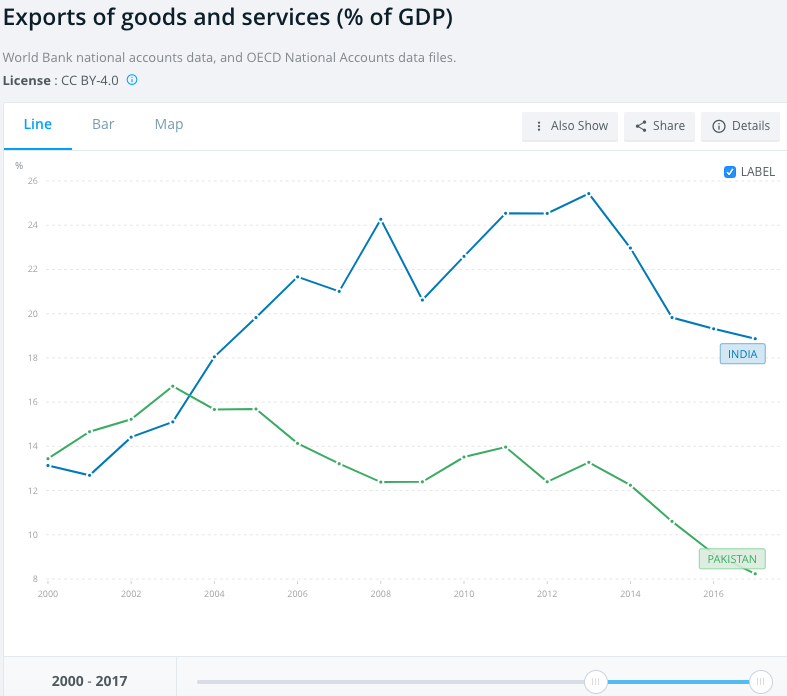
The bulk of Pakistan's exports consist of low value commodities like chadar, chawal and chamra (textiles, rice and leather). These exports have declined from about 15% to about 8% of GDP since 2003. Pakistan's trade deficits are growing at an alarming rate as the imports continue to far outstrip exports. This situation is not sustainable. What must Pakistan do to improve it? What can Pakistan do to avoid recurring balance of payments crises? How can Pakistan diversify and grow its exports to reduce the gaping trade gap? How can Pakistan's closest ally China help? Can China invest in export oriented industries and open up its huge market for exports from Pakistan? Let's explore answers to these question.
East Asia's Experience:
East Asian nations have greatly benefited from major investments made by the United States and Europe in export-oriented industries and increased access to western markets over the last several decades. Asian Tigers started with textiles and then switched to manufacturing higher value added consumer electronics and high tech products. Access to North American and European markets boosted their export earnings and helped them accumulate large foreign exchange reserves that freed them from dependence on the IMF and other international financial institutions. China, too, has been a major beneficiary of these western policies. All have significantly enhanced their living standards.
Chinese Investment and Trade:
Pakistan needs similar investments in export-oriented industries and greater access to major markets. Given the end of the Cold War and changing US alliances, it seems unlikely that the United States would help Pakistan deal with the difficulties it faces today.
China sees Pakistan as a close strategic ally. It is investing heavily in the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) which includes China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC). A recent opinion piece by Yao Jing, the Chinese Ambassador in Pakistan, published in the state-owned China Daily, appears to suggest that China is prepared to offer such help. Here are two key excerpts from the opinion piece titled "A community of shared future with Pakistan":
1. China will actively promote investment in Pakistan. The Chinese government will firmly promote industrial cooperation, expand China's direct investment in Pakistan, and encourage Chinese enterprises to actively participate in the construction of special economic zones. Its focus of cooperation will be upgrading Pakistan's manufacturing capacity and expanding export-oriented industries.
2. China will also actively expand its imports from Pakistan. In November, China will hold the first China International Import Expo in Shanghai, where, as one of the "Chief Guest" countries, Pakistan has been invited to send a large delegation of exporters and set up exhibitions at both the national and export levels. It is hoped that Pakistan will make full use of this opportunity to promote its superior products to China. The Chinese side will also promote cooperation between the customs and quarantine authorities of both countries to facilitate the further opening-up of China's agricultural product market to Pakistan. China will, under the framework of free trade cooperation between the two countries, provide a larger market share for Pakistani goods, and strengthen cooperation and facilitate local trade between Gilgit-Baltistan and China's Xinjiang Uygur autonomous region. And China will take further visa facilitation measures to encourage more Pakistani businesspeople to visit China.
Pakistan's Role:
Pakistan needs to take the Chinese Ambassador Yao Jing's offer to increase Chinese investments and open up China's market for imports from Pakistan. Pakistan's new government led by Prime Minister Imran Khan should take immediate steps to pursue the Chinese offer. Finance Minister Asad Umar needs to form a high-powered team of top bureaucrats and leading businessmen to develop a comprehensive plan to attract investments in export-oriented industries and diversify and grow exports to China and other countries. Pakistan must make full use of its vast network of overseas diplomatic missions to promote investment and trade.
Summary:
Pakistani currency has seen about 25% decline in value against the US dollar since January 2018. As a result of this devaluation, the minimum monthly wage in Pakistan has dropped from $136 last year to $107 now while in Bangladesh has seen it increased from $64 last year to $95 today. Renaissance Capital projects a further 10% depreciation this year. While this can help Pakistan's RMG exports in the short term, it is not good long term strategy. Competing on cost alone is a race to the bottom. Pakistan's manufactured exports per capita have declined in the last decade. Pakistan's exports have declined from about 15% of GDP to about 8% since 2003. The nation's trade deficits are growing at an alarming rate as the imports continue to far outstrip exports. This situation is not sustainable. Chinese Ambassador Yao Jing has offered a helping hand to increase Chinese investment and trade in Pakistan. Pakistan's new government led by Prime Minister Imran Khan should take the Chinese Ambassador's plan seriously. Finance Minister Asad Umar needs to form a high-powered team of top bureaucrats and leading businessmen on a comprehensive plan to attract investments in export-oriented industries and diversify and grow high-value exports to China and other countries.
https://www.riazhaq.com/2019/01/pakistan-garment-industry-becoming-more.html
Low wages and trade deals with Western nations have helped Bangladesh build a $30 billion ready-made garments (RMG) industry that accounts for 80% of country's exports. Bangladesh is the world's second largest RMG exporter after China. Rising monthly wages of Bangladesh garment worker in terms of US dollars are now catching up with the minimum wage in Pakistan, especially after recent Pakistani rupee devaluation. Minimum monthly wage in Pakistan has declined from $136 last year to $107 now while Bangladesh has seen it increase from $64 last year to $95 today. Western garment buyers, known for their relentless pursuit of the lowest labor costs, will likely diversify their sources by directing new investments to Pakistan and other nations. Competing on low cost alone may prove to be a poor long term exports strategy for both countries. Greater value addition with diverse products and services will be necessary to remain competitive as wages rise in both countries.

Minimum Monthly Wages in US$ Market Exchange Rate
Wage Hike in Bangladesh:
The government in Dhaka announced in September that the minimum wage for garment workers would increase by up to 51% this year to 8,000 taka ($95) a month, up from $64 a year ago, according to Renaissance Capital. But garment workers union leaders say that increase will benefit only a small percentage of workers in the sector, which employs 4 million in the country of 165 million people, according to Reuters. Bangladesh government promised this week it would consider demands for an increase in the minimum wage, after clashes between police and protesters killed one worker and wounded dozens.
Monthly Minimum Wages in US$. Source: Renaissance Capital
Pakistan Wage Decline:
Pakistani currency has seen about 25% decline in value against the US dollar since January 2018. As a result of this devaluation, the minimum monthly wage in Pakistan has dropped from $136 last year to $107 now while Bangladesh has seen it increase from $64 last year to $95 today. Renaissance Capital projects a further 10% depreciation in Pakistani rupee this year.
Race to the Bottom?
Competing on cost alone is like engaging in the race to the bottom. Neither Pakistan nor Bangladesh can count on being lowest cost producers in the long run. What must they do to grow their exports in the future? The only viable option for both is to diversify their products and services and add greater value to justify higher prices.
Pakistan's Export Performance:
The bulk of Pakistan's exports consist of low value commodities like chadar, chawal and chamra (textiles, rice and leather). These exports have declined from about 15% to about 8% of GDP since 2003. Pakistan's trade deficits are growing at an alarming rate as the imports continue to far outstrip exports. This situation is not sustainable. What must Pakistan do to improve it? What can Pakistan do to avoid recurring balance of payments crises? How can Pakistan diversify and grow its exports to reduce the gaping trade gap? How can Pakistan's closest ally China help? Can China invest in export oriented industries and open up its huge market for exports from Pakistan? Let's explore answers to these question.

East Asia's Experience:
East Asian nations have greatly benefited from major investments made by the United States and Europe in export-oriented industries and increased access to western markets over the last several decades. Asian Tigers started with textiles and then switched to manufacturing higher value added consumer electronics and high tech products. Access to North American and European markets boosted their export earnings and helped them accumulate large foreign exchange reserves that freed them from dependence on the IMF and other international financial institutions. China, too, has been a major beneficiary of these western policies. All have significantly enhanced their living standards.
Chinese Investment and Trade:
Pakistan needs similar investments in export-oriented industries and greater access to major markets. Given the end of the Cold War and changing US alliances, it seems unlikely that the United States would help Pakistan deal with the difficulties it faces today.
China sees Pakistan as a close strategic ally. It is investing heavily in the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) which includes China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC). A recent opinion piece by Yao Jing, the Chinese Ambassador in Pakistan, published in the state-owned China Daily, appears to suggest that China is prepared to offer such help. Here are two key excerpts from the opinion piece titled "A community of shared future with Pakistan":
1. China will actively promote investment in Pakistan. The Chinese government will firmly promote industrial cooperation, expand China's direct investment in Pakistan, and encourage Chinese enterprises to actively participate in the construction of special economic zones. Its focus of cooperation will be upgrading Pakistan's manufacturing capacity and expanding export-oriented industries.
2. China will also actively expand its imports from Pakistan. In November, China will hold the first China International Import Expo in Shanghai, where, as one of the "Chief Guest" countries, Pakistan has been invited to send a large delegation of exporters and set up exhibitions at both the national and export levels. It is hoped that Pakistan will make full use of this opportunity to promote its superior products to China. The Chinese side will also promote cooperation between the customs and quarantine authorities of both countries to facilitate the further opening-up of China's agricultural product market to Pakistan. China will, under the framework of free trade cooperation between the two countries, provide a larger market share for Pakistani goods, and strengthen cooperation and facilitate local trade between Gilgit-Baltistan and China's Xinjiang Uygur autonomous region. And China will take further visa facilitation measures to encourage more Pakistani businesspeople to visit China.
Pakistan's Role:
Pakistan needs to take the Chinese Ambassador Yao Jing's offer to increase Chinese investments and open up China's market for imports from Pakistan. Pakistan's new government led by Prime Minister Imran Khan should take immediate steps to pursue the Chinese offer. Finance Minister Asad Umar needs to form a high-powered team of top bureaucrats and leading businessmen to develop a comprehensive plan to attract investments in export-oriented industries and diversify and grow exports to China and other countries. Pakistan must make full use of its vast network of overseas diplomatic missions to promote investment and trade.
Summary:
Pakistani currency has seen about 25% decline in value against the US dollar since January 2018. As a result of this devaluation, the minimum monthly wage in Pakistan has dropped from $136 last year to $107 now while in Bangladesh has seen it increased from $64 last year to $95 today. Renaissance Capital projects a further 10% depreciation this year. While this can help Pakistan's RMG exports in the short term, it is not good long term strategy. Competing on cost alone is a race to the bottom. Pakistan's manufactured exports per capita have declined in the last decade. Pakistan's exports have declined from about 15% of GDP to about 8% since 2003. The nation's trade deficits are growing at an alarming rate as the imports continue to far outstrip exports. This situation is not sustainable. Chinese Ambassador Yao Jing has offered a helping hand to increase Chinese investment and trade in Pakistan. Pakistan's new government led by Prime Minister Imran Khan should take the Chinese Ambassador's plan seriously. Finance Minister Asad Umar needs to form a high-powered team of top bureaucrats and leading businessmen on a comprehensive plan to attract investments in export-oriented industries and diversify and grow high-value exports to China and other countries.
https://www.riazhaq.com/2019/01/pakistan-garment-industry-becoming-more.html
Last edited by a moderator: